The organisms commonly known as blue-green algae have proliferated much more rapidly than other algae in lakes across North America and Europe over the past two centuries – and in many cases the rate of increase has sharply accelerated since the mid-20th century, according to an international team of researchers led by scientists at McGill University.

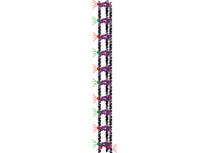
Researchers at McGill University have developed a new, low-cost method to build DNA nanotubes block by block – a breakthrough that could help pave the way for scaffolds made from DNA strands to be used in applications such as optical and electronic devices or smart drug-delivery systems.

Researchers from Canada, the UK, Sweden and the US have discovered more than 30 genes that strongly affect an antibody involved in allergies and asthma. Some of the genes could provide targets for drugs to treat those conditions, according to the international team’s study, published online in Nature on Feb. 18.
The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) announced 78 Strategic Project Grants today at the University of New Brunswick, including 10 for McGill University researchers totaling nearly $4.7 million.

Magicians have astonished audiences for centuries by subtly, yet powerfully, influencing their decisions. But there has been little systematic study of the psychological factors that make magic tricks work.

The Great Lakes have been invaded by more non-native species than any other freshwater ecosystem in the world. In spite of increasing efforts to stem the tide of invasion threats, the lakes remain vulnerable, according to scientists from McGill University and colleagues in Canada and the United States.
