Synthetic tissue can repair hearts, muscles, and vocal cords
Combining knowledge of chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering, scientists from McGill University develop a biomaterial tough enough to repair the heart, muscles, and vocal cords, representing a major advance in regenerative medicine.
“People recovering from heart damage often face a long and tricky journey. Healing is challenging because of the constant movement tissues must withstand as the heart beats. The same is true for vocal cords. Until now there was no injectable material strong enough for the job,” says Guangyu Bao, a PhD candidate in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at McGill University.
The team, led by Professor Luc Mongeau and Assistant Professor Jianyu Li, developed a new injectable hydrogel for wound repair. The hydrogel is a type of biomaterial that provides room for cells to live and grow. Once injected into the body, the biomaterial forms a stable, porous structure allowing live cells to grow or pass through to repair the injured organs.
“The results are promising, and we hope that one day the new hydrogel will be used as an implant to restore the voice of people with damaged vocal cords, for example laryngeal cancer survivors,” says Guangyu Bao.

Illustration shows the use of injectable hydrogel as an implant to fill a wound and to restore the voice. Credit: Sepideh Mohammadi
Putting it to the test
The scientists tested the durability of their hydrogel in a machine they developed to simulate the extreme biomechanics of human vocal cords. Vibrating at 120 times a second for over 6 million cycles, the new biomaterial remained intact while other standard hydrogels fractured into pieces, unable to deal with the stress of the load.
“We were incredibly excited to see it worked perfectly in our test. Before our work, no injectable hydrogels possessed both high porosity and toughness at the same time. To solve this issue, we introduced a pore-forming polymer to our formula,” says Guangyu Bao.
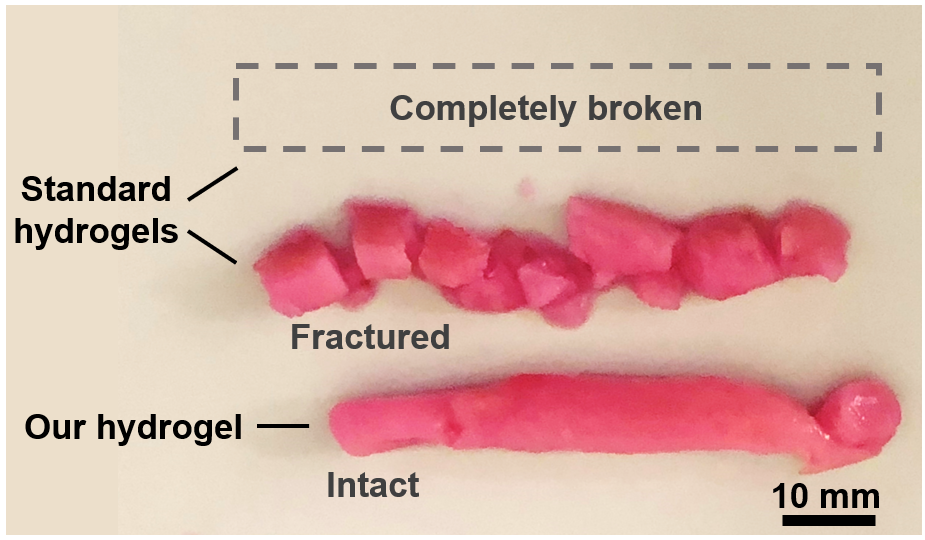
The researchers tested three different hydrogels using the vocal cord bioreactor. While the new hydrogel remained stable, the two standard hydrogels, which represent most existing injectable hydrogels, did not survive the test. Credit: Sareh Taheri
The innovation also opens new avenues for other applications like drug delivery, tissue engineering, and the creation of model tissues for drug screening, the scientists say. The team is even looking to use the hydrogel technology to create lungs to test COVID-19 drugs.
“Our work highlights the synergy of materials science, mechanical engineering and bioengineering in creating novel biomaterials with unprecedented performance. We are looking forward to translating them into the clinic”, said Professor Jianyu Li, who holds the Canada Research Chair in Biomaterials and Musculoskeletal Health.
The vocal cord bioreactor simulates the biomechanics of vocal cords to test the hydrogels. Credit: Guangyu Bao
|
About this study “Injectable, pore-forming, perfusable double-network hydrogels resilient to extreme biomechanical stimulations” by Sareh Taheri, Guangyu Bao, Zixin He, Sepideh Mohammadi, Hossein Ravanbakhsh, Larry Lessard, Jianyu Li, and Luc Mongeau was published in Advanced Science. |
About McGill University
Founded in Montreal, Quebec, in 1821, McGill University is Canada’s top ranked medical doctoral university. McGill is consistently ranked as one of the top universities, both nationally and internationally. It is a world-renowned institution of higher learning with research activities spanning three campuses, 11 faculties, 13 professional schools, 300 programs of study and over 40,000 students, including more than 10,200 graduate students. McGill attracts students from over 150 countries around the world, its 12,800 international students making up 31% of the student body. Over half of McGill students claim a first language other than English, including approximately 19% of our students who say French is their mother tongue.