Heat Transfer plays a key role in the development of almost every emerging technology. For instance, it is well established that one of the main factors inhibiting the development of even faster microchips that exist today is the effective removal of the heat generated within the chips. The heat generation increases as the chip speed increases or the size decreases.
One of the many reasons that the use of high temperature superconductors is currently limited is because of the inability to maintain a constant enough temperature for them to operate; the temperature band in which these materials become superconducting is very narrow. Also the thermal efficiency of turbines increases as the operating temperature increases; however, the inability to effectively cool the turbine blades so that they do not melt or sustain damage has prevented their commercial introduction. These situations and many more rely on adroit application of heat transfer principles.
The scenarios above primarily involve heat transfer through two modes: conduction and convection. A thorough understanding of these modes will aid in attacking heat transfer issues in many diverse situations. To gain this understanding, it is important to have a feel for heat transfer in several basic situations like those presented in the following three experiments:
-
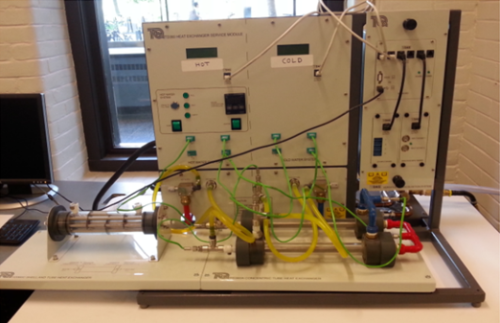
Heat Exchanger
Objectives:
- To determine the heat transfer rate between a flow of hot water and a flow of cold water as they pass through two types of heat exchangers in a parallel and counter flow manner.
- To determine and compare the experimental and theoretical overall heat transfer coefficients and the heat exchanger effectiveness
-
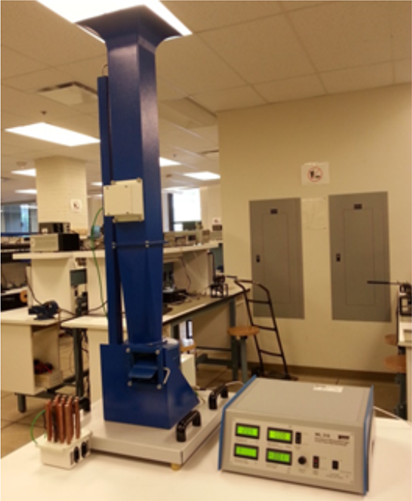
Cross Flow Heat Exchanger
Objectives:
- Investigation of heat convection processes
- Comparison of the heat transfer coefficient of different heating elements
- Make a comparison between different heating elements
- Demonstration of the relationship between heat transfer, area of heat transfer and flow velocity

-
Heat Conduction in Solids
Objectives:
- To study the heat conduction in different solids
- To determine the thermal conductivity of different materials for one or multiple layers
- To compare the obtained conductive heat transfer coefficients with the published ones, find the error, and discuss the possible sources of the error
