Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It spreads through the air when individuals with active TB cough, speak, or sneeze.
Leading cause of death
Globally, TB has returned as the leading cause of death from an infectious disease (after three years of it being COVID-19. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) (the McGill International TB Centre is a WHO Collaborating Centre in tuberculosis), a total of 1.25 million people died from TB in 2023. It was also the leading killer of people with HIV and a major cause of deaths related to antimicrobial resistance.
In 2023, the WHO estimates that 10.8 million people fell ill with TB worldwide, including 6.0 million men, 3.6 million women and 1.3 million children. TB is present in all countries and age groups.
Preventing TB’s spread
TB continues to spread largely because it is often diagnosed late, and there is currently no effective vaccine to prevent it. Although antibiotics can prevent TB before it progresses to active disease, they are prescribed to only a small proportion of those who could benefit. Once TB becomes active, treatment is lengthy, complicated, and can cause serious side effects. There is a pressing need for more research to develop faster, more accurate diagnostic tools and safer, shorter treatment options.
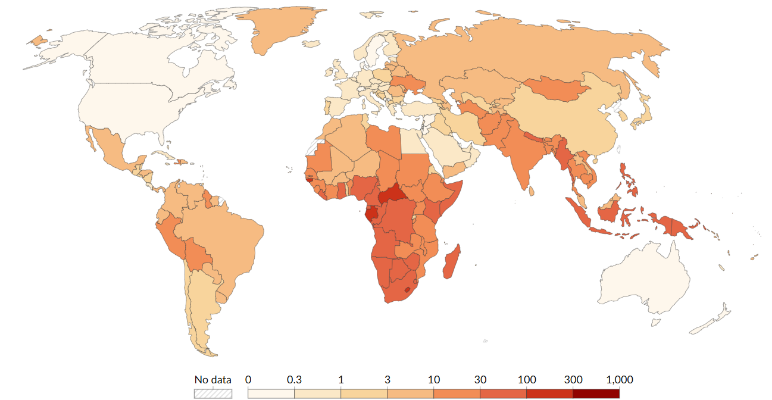
Tuberculosis death rate, 2023
Data source: WHO (2024); Population based on various sources (2024).