Glossary of Terms of Interprofessional Practice
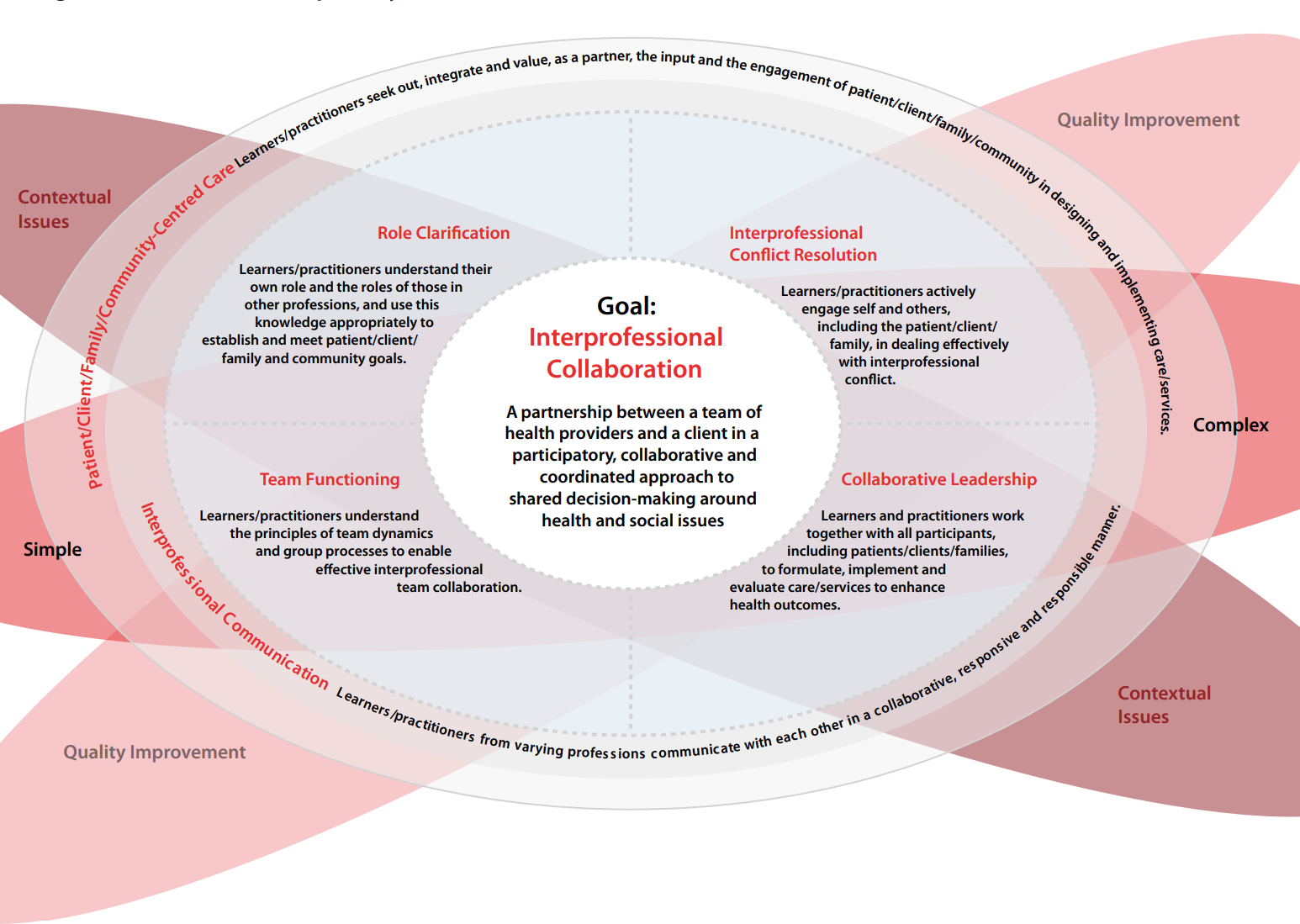
Interprofessional Collaboration
Interprofessional collaboration is a process of developing and maintaining a partnership between a team of healthcare providers and patients/clients/families and communities to enable optimal health outcomes. It requires a participatory, collaborative and coordinated approach to shared decision-making around health and social issues and includes respect, trust, communication and shared leadership.
Interprofessional Collaborative Practice (IPCP)
Interprofessional collaborative practice is essential for improvement in patient/client/ family and community health outcomes. It promotes the active participation of each health care professional in patient care within the clinical setting. It enhances patient and family-centred goals and values, provides mechanisms for continuous communication among caregivers, optimizes professional participation in clinical decision-making and fosters respect for contributions made by all professionals. (Health Canada 2003).
Team Functioning
Team functioning describes an interdependent relationship that exists between members of a team. It is an application of collaboration of relationships and interactions that take place between coworkers. Learners/practitioners understand the principles of teamwork dynamics and group/team processes to enable effective interprofessional collaboration.
Patient/Client/Family/Community-Centred Care
Learners/practitioners seek out, integrate and value, as a partner, the input, and the engagement of the patient/client/family/community in designing and implementing care/services. It enhances patient and family or community-centred goals and values, provides mechanisms for continuous communication among caregivers through active participation and shared decision-making.
Role Clarification
Role clarification occurs when learners/practitioners understand their own role and the roles of others and use this knowledge appropriately to establish and achieve patient/client, family, and community goals. Students/practitioners need to clearly articulate their roles, knowledge, and skills within the context of their clinical work. Each must have the ability to listen to other professionals to identity where unique knowledge and skills are held, and where shared knowledge and skills occur. (CIHC, 2010)
Collaborative Leadership
Collaborative leadership supports interprofessional collaborative practice as practice learners/ practitioners understand the need for and provide leadership to support effective team processes. It requires the acknowledgement and respect for shared decision making but also for continued individual accountability for one’s own actions, responsibilities and roles as explicitly defined within one’s scope of practice. Within collaborative or shared leadership, learners/ practitioners support the choice of a leader depending on the context of the situation and targeted outcomes.
Interprofessional Conflict Resolution
Interprofessional Conflict resolution supports interprofessional collaborative practice and requires active engagement and reflection of learners/practitioners and client/patient/family partners to constructively address disagreements or conflicts as they arise. Within a safe environment for exchange of differing viewpoints, team members can effectively work towards a resolution of disagreement through identified or acknowledged strategies or guidelines.