The results of the study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, point to the first known cause of aortic stenosis and to a potential treatment to prevent this disease. “We found that an unusual type of cholesterol called Lipoprotein (a) or Lp(a) – that is not normally screened for in current clinical practice – appears to be a cause of aortic valve disease,” says Dr. George Thanassoulis, one of the co-lead authors of the study, who is also director of preventive and genomic cardiology at the MUHC and an Assistant Professor in Medicine at McGill University. “High levels of this type of cholesterol are predicted primarily by an individual’s genetic make-up with only modest influence from lifestyle or other factors.”

How does Canada foster and grow its celebrities and success? Is Canada efficient enough at spotting talent and supporting it through incubation and lift-off? The McGill Institute for the Study of Canada (MISC) will examine what it means to have a career in Canada in three sectors: culture/entertainment, high-tech and sports/athletics at its annual conference, “Lifting Off and Flying High: Talent and Success in Canada”. The two-day event will be held at the Omni Mont-Royal Hotel, 1050 Sherbrooke St. W., Montreal, on February 11-12, 2013.

Please note that McGill University will be giving an update on the flooding experienced on the downtown campus since yesterday.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), commonly known as lupus, is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks healthy tissue such as the skin, joints, kidneys and the brain, leading to inflammation and lesions. The disease affects about 1 in 2000 Canadians, particularly women. Previous research has suggested that lupus patients have an increased risk of developing cancer, particularly lymphoma. Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer that occurs when cells called lymphocytes, which usually help protect the body from infection and disease, begin growing and multiplying uncontrollably leading to tumor growth.

One lies hidden inside a coffin. Another has his face exposed with hands extended at his sides. A third wears a mask over her face. They are three human Egyptian mummies that have been trapped in the manner they held when laid to rest nearly 2,000 years ago. And now we can reveal what they might have looked like.
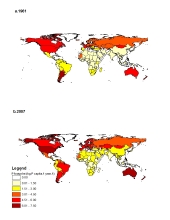
Dietary changes since the early 1960s have fueled a sharp increase in the amount of mined phosphorus used to produce the food consumed by the average person over the course of a year, according to a new study led by researchers at McGill University. Between 1961 and 2007, rising meat consumption and total calorie intake underpinned a 38% increase in the world’s per capita “phosphorus footprint,” the researchers conclude in a paper published online in Environmental Research Letters.
From early disease detection to better drug design and more efficient nanoelectronics – three McGill research projects share close to $11 million in awards from the CFI

Researchers at McGill University and the Research Center for Molecular Medicine (CeMM) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences have discovered the molecular blueprint behind the IFIT protein. This key protein enables the human immune system to detect viruses and prevent infection by acting as foot soldiers guarding the body against infection. They recognize foreign viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) produced by the virus and act as defender molecules by potentially latching onto the genome of the virus and preventing it from making copies of itself, blocking infection. The findings are a promising step towards developing new drugs for combatting a wide range of immune system disorders.

A new study by McGill University’s Division of Cancer Epidemiology will test a revolutionary way of preventing the transmission of the human papillomavirus (HPV) through the use of a topical gel applied during sexual activity.
Researchers at McGill University have discovered that a key regulator of energy metabolism in cancer cells known as the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) may play a crucial role in restricting cancer cell growth. AMPK acts as a “fuel gauge” in cells; AMPK is turned on when it senses changes in energy levels, and helps to change metabolism when energy levels are low, such as during exercise or when fasting. The researchers found that AMPK also regulates cancer cell metabolism and can restrict cancer cell growth.

As embryos develop and grow, from a single-cell egg to a fully functional body, they must form organs that are in proportion to the overall size of the embryo. The exact mechanism underlying this fundamental characteristic, called scaling, is still unclear. But researchers from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Heidelberg, Germany, and McGill University in Montreal are one step closer to understanding it.

The Green Revolution has stagnated for key food crops in many regions of the world, according to a study published in Nature Communications by scientists with the University of Minnesota’s Institute on the Environment and McGill University.
